# http 传输相关
# 搭建 Http 服务
首先需要引入 http 模块,使用它的 createServer 方法来创建一个 http 服务。createServer 方法的形参是一个回调函数,在每次接收到请求时被执行。该回调函数有两个形参,第一个是请求对象,第二个是响应对象。在最后,需要使用 listen 方法来监听一个端口(第一个形参),服务就绪时会执行第二个形参(回调函数)。
// 引入http模块
const http = require("http");
// 服务会部署在哪个端口
const port = 8000;
// 创建一个服务
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
// 状态码
res.statusCode = 200;
// 数据形式
res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain");
// 返回给客户端的信息
res.end("你好世界\n");
});
// 服务就绪
server.listen(port, () => {
console.log("服务已启动");
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 处理 get 请求
GET 请求是客户端向服务端请求查询一些数据,可以在 URL 带上查询参数。浏览器 URL 直接回车请求就是一个 GET 请求。请看下面这个例子,浏览器输入http://localhost:8000/?key=1&name=2并回车,req.method 的值是GET,req.url的值是/?key=1&name=2,经过 URLSearchParams 处理过后,返回到页面的值是一个 JSON 字符串{"key":"1","name":"2"}。
// 引入http模块
const http = require("http");
const { URL } = require("url");
// 服务会部署在哪个端口
const port = 8000;
// 创建一个服务
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
// 什么类型的请求,请求的地址
console.log("req.method", req.method);
console.log("req.url", req.url);
// URL相关信息
const url = new URL(req.url, `http://${req.headers.host}`);
const resData = {};
// 显示键/值对,处理成对象
for (const item of url.searchParams) {
resData[item[0]] = item[1];
}
// 状态码
res.statusCode = 200;
// 数据形式
res.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/json");
// 返回给客户端的信息
res.end(JSON.stringify(resData));
});
// 服务就绪
server.listen(port, () => {
console.log("服务已启动");
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
当 request.url 为 '/status?name=ryan' 且 request.headers.host 为 'localhost:3000' 时:
$ node
> new URL(request.url, `http://${request.headers.host}`)
URL {
href: 'http://localhost:3000/status?name=ryan',
origin: 'http://localhost:3000',
protocol: 'http:',
username: '',
password: '',
host: 'localhost:3000',
hostname: 'localhost',
port: '3000',
pathname: '/status',
search: '?name=ryan',
searchParams: URLSearchParams { 'name' => 'ryan' },
hash: ''
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# 处理 post 请求
POST 请求是客户端向服务端传递一些数据,这些数据大多数用于修改更新服务端存储数据。POST 请求可以使用 ajax/axios 来发送,如果不想写代码,可以使用谷歌应用商店里的postman (opens new window)来模拟发送 POST 请求。
node 处理 POST 请求的处理与 GET 不一样,它的接收数据可能会很大,所以它使用了req.on('data')来一直接收数据,在数据接收完后有req.on('end')来收尾。
// 引入http模块
const http = require("http");
// 服务会部署在哪个端口
const port = 8000;
// 创建一个服务
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
if (req.method === "POST") {
console.log("req Content-Type", req.headers["content-type"]);
let postData = "";
// 接收数据
req.on("data", (chunk) => {
postData += chunk;
});
// 数据接收完毕
req.on("end", () => {
console.log("postData", postData);
// 状态码
res.statusCode = 200;
// 数据形式
res.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/json");
// 返回给客户端的信息
res.end(JSON.stringify(postData));
});
}
});
// 服务就绪
server.listen(port, () => {
console.log("服务已启动");
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
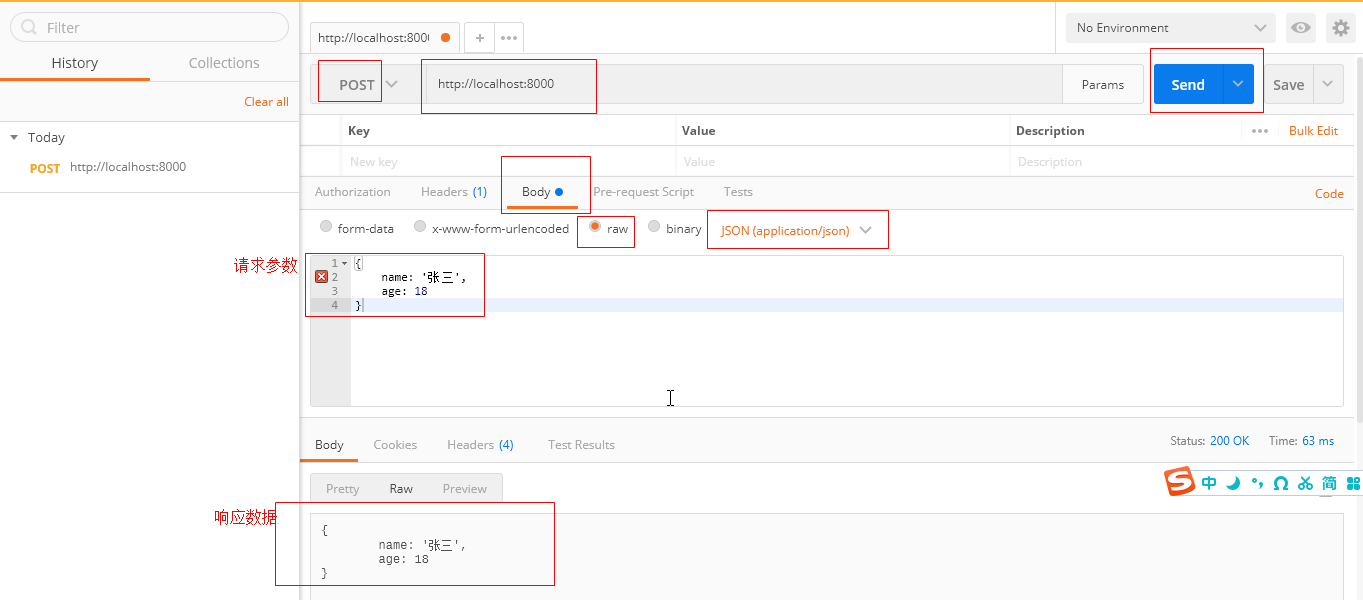
打开谷歌浏览器,进入chrome://apps,点击Postman,我们在以下界面填写相应的数据。地址栏里填写完整的地址,包括端口号;点击 Body,然后选择 raw,然后选择数据类型为JSON(application/json);在 textArea 里输入请求数据例如{name:'张三',age:18},最后点击 Send 就可以发送一个 POST 请求了。(下图的请求参数是“Bad String”,字符串得使用双引号,并且这个 key 也得用双引号包裹)
看一下同时处理 GET 和 POST 请求:
// 引入http模块
const http = require("http");
const { URL } = require("url");
// 服务会部署在哪个端口
const port = 8000;
// 创建一个服务
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
// 什么请求
const method = req.method;
// 数据形式
res.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/json");
// 状态码
res.statusCode = 200;
// URL相关信息
const url = new URL(req.url, `http://${req.headers.host}`);
if (method === "GET") {
const resData = {};
for (const item of url.searchParams) {
resData[item[0]] = item[1];
}
// 返回给客户端的信息
res.end(JSON.stringify(resData));
} else if (method === "POST") {
let postData = "";
// 接收数据
req.on("data", (chunk) => {
postData += chunk;
});
// 数据接收完毕
req.on("end", () => {
// 返回给客户端的信息
res.end(JSON.stringify(postData));
});
}
});
// 服务就绪
server.listen(port, () => {
console.log("服务已启动");
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40